PDFвҖҢ:вҖҢШҜШ§ШұШҜ
ЩҶЩ…ЩҲЩҶЩҮ Ъ©ШҜ: ШҜШ§ШұШҜ
Щ…ЩӮШҜЩ…ЩҮ
ШЁШ§ ЪҜШіШӘШұШҙ Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ Ш§ШІ ЩғШ§Щ…ЩҫЩҠЩҲШӘШұ ШҜШұ ШЁШіЩҠШ§ШұЩҠ Ш§ШІ Ш§Щ…ЩҲШұ ШұЩҲШІЩ…ШұЩҮ Ш§ЩҶШіШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ ШіШ§ШІЪҜШ§Шұ ШЁЩҲШҜЩҶ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩҮШ§ ШЁШ§ ШіЩ„ЩҠЩӮЩҮ ЩғШ§ШұШЁШұШ§ЩҶ ШЁЩҮ ЩҠЩғЩҠ Ш§ШІ ЩҶЩҠШ§ШІ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Ш§ШөЩ„ЩҠ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ ЩғШ§Щ…ЩҫЩҠЩҲШӘШұЩҠ ШӘШЁШҜЩҠЩ„ ШҙШҜЩҮ Ш§ШіШӘ. ШЁШҜЩҲЩҶ ШҙЩғ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҲ ЩҒШұЩҮЩҶЪҜ ЩҠЩғЩҠ Ш§ШІ Щ…ЩҮЩ… ШӘШұЩҠЩҶ Ш№ЩҲШ§Щ…Щ„ ШҜШұ Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ Ш§ШұШӘШЁШ§Ш· ЩҶШІШҜЩҠЩғ ШЁЩҠЩҶ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩҲ ЩғШ§ШұШЁШұ ШЁЩҮ ШҙЩ…Ш§Шұ Щ…ЩҠ ШұЩҲШҜ ЩҲ ЩҶЩӮШҙЩҠ ШәЩҠШұ ЩӮШ§ШЁЩ„ Ш§ЩҶЩғШ§Шұ ШҜШұ Щ…ЩҠШІШ§ЩҶ Щ…ЩҲЩҒЩӮЩҠШӘ ЩҠЩғ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ШЁЩҮ Ш№ЩҮШҜЩҮ ШҜШ§ШұШҜ. Ш§ШІ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШұЩҲ ШҜШұ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ЩҶЩҲШҙШӘЩҮ ШӘЩ„Ш§Шҙ ШЁШұ ШўЩҶ Ш§ШіШӘ ШӘШ§ ЩҠЩғЩҠ Ш§ШІ ШіШ§ШҜЩҮ ШӘШұЩҠЩҶ ЩҲ ШҜШұ Ш№ЩҠЩҶ ШӯШ§Щ„ ЩғШ§ШұШ§ ШӘШұЩҠЩҶ ШұШ§ЩҮ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…Щ…ЩғЩҶ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ ЪҶЩҶШҜ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶЩҮ ШЁШ§ Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ Ш§ШІ ШӘЩғЩҶЩҲЩ„ЩҲЪҳЩҠ WPF ШўЩ…ЩҲШІШҙ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҮ ШҙЩҲШҜ.
Щ…ШұЩҲШұЩҠ ШЁШұ ШұЩҲШҙ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…ЩҲШ¬ЩҲШҜ
ЩҮЩ…ЩҲШ§ШұЩҮ ШұЩҲШҙ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…Ш®ШӘЩ„ЩҒЩҠ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ЩҫЩҠШ§ШҜЩҮ ШіШ§ШІЩҠ ЩҠЩғ Ш§ЩҠШҜЩҮ ШҜШұ ШҜЩҶЩҠШ§ЩҠ ЩҶШұЩ… Ш§ЩҒШІШ§Шұ ЩҲШ¬ЩҲШҜ ШҜШ§ШұШҜ ЩғЩҮ ЩҮШұ ШұЩҲШҙ ШұШ§ Щ…ЩҠ ШӘЩҲШ§ЩҶ ШЁШұ ШӯШіШЁ ЩҶЩҠШ§ШІ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ ЩӮШұШ§Шұ ШҜШ§ШҜ. ШҜШұ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…ШЁШӘЩҶЩҠ ШЁШұ WPF Щ…Ш№Щ…ЩҲЩ„Ш§ Ш§ШІ ШҜЩҲ ШұЩҲШҙ Ш№Щ…ШҜЩҮ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ Щ…ЩҶШёЩҲШұ Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ:
1- Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ Ш§ШІ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ .resx
ШҜШұ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШұЩҲШҙ ЩғЩҮ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Win App ЩҶЩҠШІ Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜШҢ Ш§Ш·Щ„Ш§Ш№Ш§ШӘ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶЩҠШ§ШІ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ЩҮШұ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ШЁЩҮ ШҙЩғЩ„ Ш¬ШҜЩҲЩ„ ЩҮШ§ЩҠЩҠ ШҜШ§ШұШ§ЩҠ ЩғЩ„ЩҠШҜ ЩҲ Щ…ЩӮШҜШ§Шұ ШҜШұ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ ЩҠЩғ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ .resx ЩҶЪҜЩҮШҜШ§ШұЩҠ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ ЩҲ ШҜШұ ШІЩ…Ш§ЩҶ Ш§Ш¬ШұШ§ЩҠ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ШЁШұ Ш§ШіШ§Ші Ш§ЩҶШӘШ®Ш§ШЁ ЩғШ§ШұШЁШұ Ш§Ш·Щ„Ш§Ш№Ш§ШӘ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶШёШұ Ш§ШІ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ .resx load ШҙШҜЩҮ ЩҲ ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠШҙ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҮ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ. ЩҠЩғЩҠ Ш§ШІ Ш¶Ш№ЩҒ ЩҮШ§ЩҠЩҠ ЩғЩҮ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШұЩҲШҙ ШҜШұ Ш№ЩҠЩҶ ШіШ§ШҜЩҮ ШЁЩҲШҜЩҶ ШҜШ§ШұШҜ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ Ш§ШіШӘ ЩғЩҮ ЩҮЩ…ЩҮ Ш§Ш·Щ„Ш§Ш№Ш§ШӘ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶЩҠШ§ШІ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ assembly Ш§ШөЩ„ЩҠ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩӮШұШ§Шұ Щ…ЩҠ ЪҜЩҠШұШҜ ЩҲ Ш§Щ…ЩғШ§ЩҶ Ш§ЩҒШІЩҲШҜЩҶ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Ш¬ШҜЩҠШҜ ШЁШҜЩҲЩҶ ШӘШәЩҠЩҠШұ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҶ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ Ш§ШөЩ„ЩҠ Щ…Щ…ЩғЩҶ ЩҶШ®ЩҲШ§ЩҮШҜ ШЁЩҲШҜ.
2- Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ Ш§ШІ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ .csv ЩғЩҮ ШЁЩҮ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ .dll ШӘШЁШҜЩҠЩ„ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲЩҶШҜ
ШҜШұ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШұЩҲШҙ ЩғЩҮ Щ…Ш®ШӘШө ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ WPF Щ…ЩҠ ШЁШ§ШҙШҜ ШЁШ§ Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ Ш§ШІ Ш§ШЁШІШ§Шұ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…ЩҲШ¬ЩҲШҜ ШҜШұ ЩғШ§Щ…ЩҫШ§ЩҠЩ„Шұ WPF ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ЩҮШұ ЩғЩҶШӘШұЩ„ ЩҠЩғ property ШЁЩҮ ЩҶШ§Щ… Uid Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ ШҙШҜЩҮ ЩҲ Щ…ЩӮШҜШ§Шұ ШҜЩҮЩҠ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ. ШіЩҫШі ШЁШ§ Ш§ШЁШІШ§Шұ ШҜЩҠЪҜШұЩҠ ( ЩғЩҮ Ш¬ШІЩҲ Ш§ШЁШІШ§Шұ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ ЩғШ§Щ…ЩҫШ§ЩҠЩ„Шұ Щ…ШӯШіЩҲШЁ ЩҶЩ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ ) Ш§ШІ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ .csproj ЩҫШұЩҲЪҳЩҮ ЩҠЩғ Ш®ШұЩҲШ¬ЩҠ Ш§ЩғШіЩ„ ШЁШ§ ЩҒШұЩ…ШӘ .csv Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ ЩғЩҮ ШҙШ§Щ…Щ„ Uid ЩҮШ§ЩҠ ЩғЩҶШӘШұЩ„ ЩҮШ§ ЩҲ Щ…ЩӮШ§ШҜЩҠШұ ШўЩҶ ЩҮШ§ Ш§ШіШӘ. ЩҫШі Ш§ШІ ШӘШұШ¬Щ…ЩҮ Щ…ШӘЩҲЩҶ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶШёШұ ШЁЩҮ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ Щ…ЩӮШөШҜ ШЁШ§ ЩғЩ…Щғ Ш§ШЁШІШ§Шұ ШҜЩҠЪҜШұЩҠ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ Ш§ЩғШіЩ„ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶШёШұ ШЁЩҮ ЩҠЩғ .net assembly ШӘШЁШҜЩҠЩ„ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ ЩҲ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ ЩҫЩҲШҙЩҮ Ш§ЩҠ ШЁШ§ ЩҶШ§Щ… culture Ш§ШіШӘШ§ЩҶШҜШ§ШұШҜ Ш°Ш®ЩҠШұЩҮ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ. ( Щ…Ш«Щ„Ш§ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҒШ§ШұШіЩҠ ЩҶШ§Щ… ЩҫЩҲШҙЩҮ fa-IR Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮШҜ ШЁЩҲШҜ ). ШІЩ…Ш§ЩҶЩҠ ЩғЩҮ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ Ш§Ш¬ШұШ§ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ ШЁШұ Ш§ШіШ§Ші culture Ш§ЩҠ ЩғЩҮ ШҜШұ ШіЩҠШіШӘЩ… Ш№Ш§Щ…Щ„ Ш§ЩҶШӘШ®Ш§ШЁ ШҙШҜЩҮ Ш§ШіШӘ ЩҲ ШҜШұ ШөЩҲШұШӘЩҠ ЩғЩҮ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ШўЩҶ culture ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ .dll Ш§ЩҠ Щ…ЩҲШ¬ЩҲШҜ ШЁШ§ШҙШҜШҢ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ Щ…ШұШЁЩҲШ· ШЁЩҮ ШўЩҶ culture ШұШ§ load Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮШҜ ЩғШұШҜ. ШЁШ§ ЩҲШ¬ЩҲШҜ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ЩғЩҮ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШұЩҲШҙ Щ…ШҙЩғЩ„ ШұЩҲШҙ ЩӮШЁЩ„ЩҠ ШұШ§ ЩҶШҜШ§ШұШҜ ЩҲ ШЁЩҠШҙШӘШұ ШЁШ§ ЩҲЩҠЪҳЪҜЩҠ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ WPF ШіШ§ШІЪҜШ§Шұ Ш§ШіШӘ Ш§Щ…Ш§ ЩҫШұЩҲШіЩҮ Ш§ЩҠ Ш·ЩҲЩ„Ш§ЩҶЩҠ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Ш§ЩҶШ¬Ш§Щ… ЩғШ§Шұ ЩҮШ§ ШҜШ§ШұШҜ ЩҲ ШЁЩҮ Ш§ШІШ§ЩҠ ЩҮШұ ШӘШәЩҠЩҠШұЩҠ ШЁШ§ЩҠШҜ ЩғЩ„ Щ…ШұШ§ШӯЩ„ ЩҮШұ ШЁШ§Шұ ШӘЩғШұШ§Шұ ШҙЩҲЩҶШҜ. ЩҮЩ…ЪҶЩҶЩҠЩҶ Щ…ШҙЩғЩ„Ш§ШӘЩҠ ШҜШұ ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠШҙ ШЁШұШ®ЩҠ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ ( Ш§ШІ Ш¬Щ…Щ„ЩҮ ЩҒШ§ШұШіЩҠ ) ШҜШұ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШұЩҲШҙ Щ…ШҙШ§ЩҮШҜЩҮ ШҙШҜЩҮ Ш§ШіШӘ.
ШұЩҲШҙ ШіЩҲЩ…!
ШұЩҲШҙ ШіЩҲЩ… Ш§Щ…Ш§ ЩғШ§Щ…Щ„Ш§ ШЁШұ ЩҫШ§ЩҠЩҮ WPF ЩҲ ШҜШұ Ш§ШөШ·Щ„Ш§Шӯ WPF-Native Щ…ЩҠ ШЁШ§ШҙШҜ. Ш§ЩҠШҜЩҮ Ш§ШІ ШўЩҶШ¬Ш§ ЩҶШ§ШҙЩҠ ШҙШҜЩҮ Ш§ШіШӘ ЩғЩҮ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ skin ШҜШұ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ WPF Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ. ШҜШұ Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Skin-Based ШЁЩҮ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШҙЩҠЩҲЩҮ Ш№Щ…Щ„ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ ЩғЩҮ skin ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶШёШұ ШЁЩҮ ШөЩҲШұШӘ style ЩҮШ§ЩҠЩҠ ШҜШұ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ resource dictionary ЩҮШ§ ЩӮШұШ§Шұ Щ…ЩҠ ЪҜЩҠШұЩҶШҜ. ШіЩҫШі ШўЩҶ resource dictionary ШЁЩҮ ШҙЩғЩ„ .dll ЩғШ§Щ…ЩҫШ§ЩҠЩ„ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ. ШҜШұ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ Ш§ШөЩ„ЩҠ ЩҶЩҠШІ ЩҮЩ…ЩҮ ЩғЩҶШӘШұЩ„ ЩҮШ§ style ЩҮШ§ЩҠШҙШ§ЩҶ ШұШ§ ШЁЩҮ ШҙЩғЩ„ dynamic resource Ш§ШІ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ ЩҠЩғ resource dictionary Щ…ШҙШ®Шө ШҙШҜЩҮ load Щ…ЩҠ ЩғЩҶЩҶШҜ. ШӯШ§Щ„ ЩғШ§ЩҒЩҠ Ш§ШіШӘ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ШӘШәЩҠЩҠШұ skinШҢ resource dictionary Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶШёШұ Ш§ШІ .dll Щ…ШҙШ®Шө load ШҙЩҲШҜ ЩҲ resource dictionary Ш§ЩҠ ЩғЩҮ ШҜШұ ШӯШ§Щ„ ШӯШ§Ш¶Шұ ШҜШұ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ Ш§ШІ ШўЩҶ Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ ШЁШ§ resource dictionary Ш§ЩҠ ЩғЩҮ load ШҙШҜЩҮ Ш¬Ш§ЩҠЪҜШІЩҠЩҶ ШҙЩҲШҜ. ЩғЩҶШӘШұЩ„ ЩҮШ§ Щ…ЩӮШ§ШҜЩҠШұ Ш¬ШҜЩҠШҜ ШұШ§ Ш§ШІ resource dictionary Ш¬ШҜЩҠШҜ ШЁЩҮ ШҙЩғЩ„ ЩғШ§Щ…Щ„Ш§ Ш®ЩҲШҜЩғШ§Шұ ШҜШұЩҠШ§ЩҒШӘ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮЩҶШҜ ЩғШұШҜ.
Ш®ЩҲШЁ! ШЁЩҮ ШіШ§ШҜЪҜЩҠ Щ…ЩҠ ШӘЩҲШ§ЩҶ Ш§ШІ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШұЩҲШҙ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ШӘШәЩҠЩҠШұ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩҶЩҠШІ Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ ЩғШұШҜ.
ЩҫЩҠШ§ШҜЩҮ ШіШ§ШІЩҠ
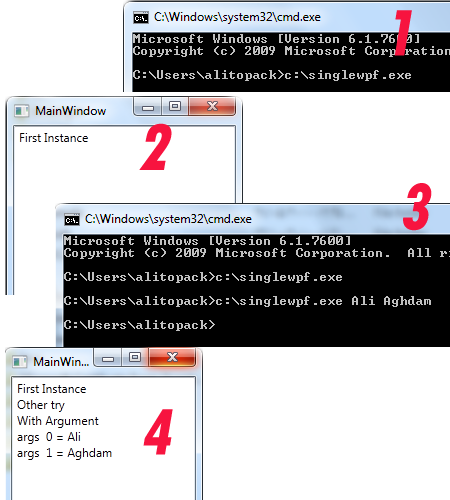
ШҜШұ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ЩӮШіЩ…ШӘ ЩҶШӯЩҲЩҮ ЩҫЩҠШ§ШҜЩҮ ШіШ§ШІЩҠ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШұЩҲШҙ ШЁШ§ Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ ЩҠЩғ ЩҶЩ…ЩҲЩҶЩҮ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ШіШ§ШҜЩҮ ЩғЩҮ ШҜШ§ШұШ§ЩҠ ШҜЩҲ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ Ш§ЩҶЪҜЩ„ЩҠШіЩҠ ЩҲ ЩҒШ§ШұШіЩҠ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮШҜ ШЁЩҲШҜ ШўЩ…ЩҲШІШҙ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҮ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲШҜ.
Ш§ШЁШӘШҜШ§ ЩҠЩғ ЩҫШұЩҲЪҳЩҮ WPF Application ШҜШұ Visual Studio 2010 Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ. ШҜШұ MainWindow ШіЩҮ ЩғЩҶШӘШұЩ„ Button ЩӮШұШ§Шұ ШҜЩҮЩҠШҜ ЩҲ ЩҠЩғ ComboBox ЩғЩҮ ЩӮШұШ§Шұ Ш§ШіШӘ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…ЩҲШ¬ЩҲШҜ ШұШ§ ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠШҙ ШҜЩҮШҜ ЩҲ ШЁШ§ Ш§ЩҶШӘШ®Ш§ШЁ ЩҠЩғ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶШҢ ЩҶЩҲШҙШӘЩҮ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ ШҜШұЩҲЩҶ Button ЩҮШ§ Щ…ШӘЩҶШ§ШіШЁ ШЁШ§ ШўЩҶ ШӘШәЩҠЩҠШұ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮЩҶШҜ ЩғШұШҜ.

ШӘЩҲШ¬ЩҮ ШҜШ§ШҙШӘЩҮ ШЁШ§ШҙЩҠШҜ ЩғЩҮ ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Button ЩҮШ§ ЩҶШЁШ§ЩҠШҜ ШЁЩҮ ШөЩҲШұШӘ Щ…ШіШӘЩӮЩҠЩ… Щ…ЩӮШҜШ§ШұЩҠ ШЁЩҮ Content ШҙШ§ЩҶ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҮ ШҙЩҲШҜ. ШЁЩ„ЩғЩҮ ШЁШ§ЩҠШҜ Щ…ЩӮШҜШ§Шұ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶШёШұ Ш§ШІ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ resource dictionary ЩғЩҮ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮЩҠЩ… ШіШ§Ш®ШӘ ШЁЩҮ ШҙЩғЩ„ dynamic ЪҜШұЩҒШӘЩҮ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮШҜ ШҙШҜ. ЩҫШі ШҜШұ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ Щ…ШұШӯЩ„ЩҮ ЩҠЩғ ResourceDictionary ШЁЩҮ ЩҫШұЩҲЪҳЩҮ Ш§Ш¶Ш§ЩҒЩҮ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮЩҠЩ… ЩғШұШҜ ЩҲ ШҜШұ ШўЩҶ resource ЩҮШ§ЩҠЩҠ ШЁЩҮ ШҙЩғЩ„ string Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮЩҠЩ… ЩғШұШҜ. ЩҮШұ resource ШҜШ§ШұШ§ЩҠ ЩҠЩғ Key Щ…ЩҠ ШЁШ§ШҙШҜ ЩғЩҮ ШЁШұ Ш§ШіШ§Ші ШўЩҶШҢ Button Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶШёШұ Щ…ЩӮШҜШ§Шұ ШўЩҶ Resource ШұШ§ load Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮШҜ ЩғШұШҜ. ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ResourceDictionary ШұШ§ Culture_en-US.xaml ЩҶШ§Щ…ЪҜШ°Ш§ШұЩҠ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ ЩҲ Щ…ЩӮШ§ШҜЩҠШұ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶШёШұ ШұШ§ ШЁЩҮ ШўЩҶ Ш§Ш¶Ш§ЩҒЩҮ ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠЩҠШҜ.
<ResourceDictionary xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:system="clr-namespace:System;assembly=mscorlib">
<system:String x:Key="button1">Hello!</system:String>
<system:String x:Key="button2">How Are You?</system:String>
<system:String x:Key="button3">Are You OK?</system:String>
</ResourceDictionary>
ШҜЩӮШӘ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ ЩғЩҮ namespace Ш§ЩҠ ЩғЩҮ ЩғЩ„Ш§Ші string ШҜШұ ШўЩҶ ЩӮШұШ§Шұ ШҜШ§ШұШҜ ШЁЩҮ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ xaml Ш§Ш¶Ш§ЩҒЩҮ ШҙШҜЩҮ Ш§ШіШӘ.
ЩҫШі Ш§ШІ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ЩғШ§Шұ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ App.xaml ШЁЩҮ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШҙЩғЩ„ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮШҜ ШЁЩҲШҜ:
<Application x:Class="BeRMOoDA.WPF.LocalizationSample.App"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
StartupUri="MainWindow.xaml">
<Application.Resources>
<ResourceDictionary>
<ResourceDictionary.MergedDictionaries>
<ResourceDictionary Source="Culture_en-US.xaml"/>
</ResourceDictionary.MergedDictionaries>
</ResourceDictionary>
</Application.Resources>
</Application>
ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Ш§ШіШӘЩҒШ§ШҜЩҮ Ш§ШІ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ resource ЩҮШ§ ШЁЩҮ Ш№ЩҶЩҲШ§ЩҶ Content ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Button ЩҮШ§ ЩҶЩҠШІ ШўЩҶ ЩҮШ§ ШұШ§ ШЁЩҮ ШөЩҲШұШӘ DynamicResourceШҢ load Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮЩҠЩ… ЩғШұШҜ:
<Button Content="{DynamicResource ResourceKey=button1}" />
<Button Content="{DynamicResource ResourceKey=button2}" />
<Button Content="{DynamicResource ResourceKey=button3}" />
ШЁШіЩҠШ§Шұ Ш®ЩҲШЁ! Ш§ЩғЩҶЩҲЩҶ ШЁШ§ЩҠШҜ ШҙШұЩҲШ№ ШЁЩҮ Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ ЩҠЩғ ResourceDictionary ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҒШ§ШұШіЩҠ ЩғЩҶЩҠЩ… ЩҲ ШўЩҶ ШұШ§ ШЁЩҮ ШөЩҲШұШӘ ЩҠЩғ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ .dll ЩғШ§Щ…ЩҫШ§ЩҠЩ„ ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠЩҠЩ….
ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ЩғШ§Шұ ЩҠЩғ ЩҫШұЩҲЪҳЩҮ Ш¬ШҜЩҠШҜ ШҜШұ ЩӮШіЩ…ШӘ WPF Ш§ШІ ЩҶЩҲШ№ User control Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ Щ…ЩҠ ЩғЩҶЩҠЩ… ЩҲ ЩҶШ§Щ… ШўЩҶ ШұШ§ Culture_fa-IR_Farsi ЩӮШұШ§Шұ Щ…ЩҠ ШҜЩҮЩҠЩ…. Щ„Ш·ЩҒШ§ ШҙЩҠЩҲЩҮ ЩҶШ§Щ…ЪҜШ°Ш§ШұЩҠ ШұШ§ ШұШ№Ш§ЩҠШӘ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ ЪҶШұШ§ ЩғЩҮ ШҜШұ Ш§ШҜШ§Щ…ЩҮ ШЁЩҮ ШўЩҶ ЩҶЩҠШ§ШІ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮЩҠЩ… ШҜШ§ШҙШӘ.
ЩҫШі Ш§ШІ Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ ЩҫШұЩҲЪҳЩҮ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ UserControl1.xaml ШұШ§ Ш§ШІ ЩҫШұЩҲЪҳЩҮ ШӯШ°ЩҒ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ ЩҲ ЩҠЩғ ResourceDictionary ШЁШ§ ЩҶШ§Щ… Culture_fa-IR.xaml Ш§Ш¶Ш§ЩҒЩҮ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ. Щ…ШӯШӘЩҲШ§ЩҠ ШўЩҶ ШұШ§ ЩҫШ§Щғ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ ЩҲ Щ…ШӯШӘЩҲШ§ЩҠ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ Culture_en-US.xaml ШұШ§ Ш§ШІ ЩҫШұЩҲЪҳЩҮ ЩӮШЁЩ„ЩҠ ШЁЩҮ ШөЩҲШұШӘ ЩғШ§Щ…Щ„ ШҜШұ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ Ш¬ШҜЩҠШҜ ЩғЩҫЩҠ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ. ШҜЩҲ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ШЁШ§ЩҠШҜ ШіШ§Ш®ШӘШ§Шұ ЩғШ§Щ…Щ„Ш§ ЩҠЩғШіШ§ЩҶЩҠ Ш§ШІ ЩҶШёШұ key ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ resource ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…ЩҲШ¬ЩҲШҜ ШҜШ§ШҙШӘЩҮ ШЁШ§ШҙЩҶШҜ. ШӯШ§Щ„Ш§ ШІЩ…Ш§ЩҶ ШӘШұШ¬Щ…ЩҮ ЩҒШұШ§ ШұШіЩҠШҜЩҮ Ш§ШіШӘ! ШұШҙШӘЩҮ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ ШҜЩ„Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮ ШұШ§ ШӘШұШ¬Щ…ЩҮ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ ЩҲ ЩҫШұЩҲЪҳЩҮ ШұШ§ build ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠЩҠШҜ.
<ResourceDictionary xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:system="clr-namespace:System;assembly=mscorlib">
<ResourceDictionary.MergedDictionaries>
<ResourceDictionary Source="Culture_fa-IR_Farsi.xaml"/>
</ResourceDictionary.MergedDictionaries>
<system:String x:Key="button1">ШіЩ„Ш§Щ…!</system:String>
<system:String x:Key="button2">ШӯШ§Щ„ШӘ ЪҶШ·ЩҲШұЩҮШҹ</system:String>
<system:String x:Key="button3">Ш®ЩҲШЁЫҢШҹ</system:String>
</ResourceDictionary>
Ш®ШұЩҲШ¬ЩҠ ЩҠЩғ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ШЁШ§ ЩҶШ§Щ… Culture_fa-IR_Farsi.dll Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮШҜ ШЁЩҲШҜ.
ШҜШұ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ Щ…ШұШӯЩ„ЩҮ ЩғШ§ШұЩҠ ЩғЩҮ ШЁШ§ЩҠШҜ Ш§ЩҶШ¬Ш§Щ… ШҜЩҮЩҠЩ… ЪҶЩҠШіШӘШҹ
ШұШ§ЩҮЩғШ§ШұЩҠ Ш§ШұШҰЩҮ ШҜЩҮЩҠЩ… ШӘШ§ ШЁШӘЩҲШ§ЩҶ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ .dll Щ…ШұШЁЩҲШ· ШЁЩҮ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ ШұШ§ ШҜШұ ШІЩ…Ш§ЩҶ Ш§Ш¬ШұШ§ЩҠ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ load ЩғШұШҜЩҮ ЩҲ ЩҶШ§Щ… ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ ШұШ§ ШҜШұ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ ComboBox Ш§ЩҠ ЩғЩҮ ШҜШ§ШұЩҠЩ… ЩҶШҙШ§ЩҶ ШҜЩҮШҜ. ШіЩҫШі ШЁШ§ Ш§ЩҶШӘШ®Ш§ШЁ ЩҮШұ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ШҜШұ ComboBoxШҢ Щ…ШӯШӘЩҲШ§ЩҠ Button ЩҮШ§ ШЁШұ Ш§ШіШ§Ші ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ Ш§ЩҶШӘШ®Ш§ШЁ ШҙШҜЩҮ ШӘШәЩҠЩҠШұ ЩғЩҶШҜ.
ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ШіЩҮЩҲЩ„ШӘ ЩғШ§ШұШҢ ЩҶШ§Щ… ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ЩҮШ§ ШұШ§ ШЁЩҮ ЪҜЩҲЩҶЩҮ Ш§ЩҠ Ш§ЩҶШӘШ®Ш§ШЁ ЩғШұШҜЩҠЩ… ЩғЩҮ ШЁШӘЩҲШ§ЩҶЩҠЩ… ШіШ§ШҜЩҮ ШӘШұ ШЁЩҮ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ЩҮШҜЩҒ ШЁШұШіЩҠЩ…. ЩҶШ§Щ… ЩҮШұ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ Ш§ШІ ШіЩҮ ШЁШ®Шҙ ШӘШҙЩғЩҠЩ„ ШҙШҜЩҮ Ш§ШіШӘ:
Culture_[standard culture notation]_[display name for this culture].dll
ЩҠШ№ЩҶЩҠ Ш§ЪҜШұ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ Culture_fa-IR_Farsi.dll ШұШ§ ШҜШұ ЩҶШёШұ ШЁЪҜЩҠШұЩҠЩ…ШҢ Culture ЩҶШҙШ§ЩҶ ШҜЩҮЩҶШҜЩҮ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ Ш§ШіШӘ ЩғЩҮ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ Щ…ШұШЁЩҲШ· ШЁЩҮ ЩҠЩғ culture Щ…ЩҠ ШЁШ§ШҙШҜ. fa-IR ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠШҙ Ш§ШіШӘШ§ЩҶШҜШ§ШұШҜ culture ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ЩғШҙЩҲШұ Ш§ЩҠШұШ§ЩҶ ЩҲ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҒШ§ШұШіЩҠ Ш§ШіШӘ ЩҲ Farsi ЩҮЩ… Щ…ЩӮШҜШ§ШұЩҠ Ш§ШіШӘ ЩғЩҮ Щ…ЩҠ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮЩҠЩ… ШҜШұ ComboBox ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠШҙ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҮ ШҙЩҲШҜ.
ЩҫЩҲШҙЩҮ Ш§ЩҠ ШЁШ§ ЩҶШ§Щ… Languages ШҜШұ ЩғЩҶШ§Шұ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ .exe ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ Ш§ЩҠШ¬Ш§ШҜ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ ЩҲ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ Culture_fa-IR_Farsi.dll ШұШ§ ШҜШұЩҲЩҶ ШўЩҶ ЩғЩҫЩҠ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ. ШӘШөЩ…ЩҠЩ… ШҜШ§ШұЩҠЩ… ЩҮЩ…ЩҮ .dll ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…ШұШЁЩҲШ· ШЁЩҮ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ ШұШ§ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ЩҫЩҲШҙЩҮ ЩӮШұШ§Шұ ШҜЩҮЩҠЩ… ШӘШ§ Щ…ШҜЩҠШұЩҠШӘ ШўЩҶ ЩҮШ§ ШіШ§ШҜЩҮ ШӘШұ ШҙЩҲШҜ.
ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ Щ…ШҜЩҠШұЩҠШӘ ШЁЩҮШӘШұ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…ШұШЁЩҲШ· ШЁЩҮ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ ЩҠЩғ ЩғЩ„Ш§Ші ШЁШ§ ЩҶШ§Щ… CultureAssemblyModel Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮЩҠЩ… ШіШ§Ш®ШӘ ЩғЩҮ ЩҮШұ object Ш§ШІ ШўЩҶ ЩҶШҙШ§ЩҶЪҜШұ ЩҠЩғ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮШҜ ШЁЩҲШҜ. ЩҠЩғ ЩғЩ„Ш§Ші ШЁШ§ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ЩҶШ§Щ… ШЁЩҮ ЩҫШұЩҲЪҳЩҮ Ш§Ш¶Ш§ЩҒЩҮ ЩғЩҶЩҠШҜ ЩҲ property ЩҮШ§ЩҠ ШІЩҠШұ ШұШ§ ШҜШұ ШўЩҶ ШӘШ№ШұЩҠЩҒ ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠЩҠШҜ:
public class CultureAssemblyModel
{
//the text will be displayed to user as language name (like Farsi)
public string DisplayText { get; set; }
//name of .dll file (like Culture_fa-IR_Farsi.dll)
public string Name { get; set; }
//standar notation of this culture (like fa-IR)
public string Culture { get; set; }
//name of resource dictionary file name inside the loaded .dll (like Culture_fa-IR.xaml)
public string XamlFileName { get; set; }
}
ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ComboBox ЩҶЩҠШІ ЩҠЩғ DataTemplate ШӘШ№ШұЩҠЩҒ Щ…ЩҠ ЩғЩҶЩҠЩ… ШӘШ§ ЩҒЩӮШ· ЩҒЩҠЩ„ШҜ DisplayText Ш§ШІ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ЩғЩ„Ш§Ші ШұШ§ ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠШҙ ШҜЩҮШҜ:
<ComboBox HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="10" VerticalAlignment="Top" MinWidth="100" Name="comboboxLanguages">
<ComboBox.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<Label Content="{Binding DisplayText}"/>
</DataTemplate>
</ComboBox.ItemTemplate>
</ComboBox>
ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ load ЩғШұШҜЩҶ ЩҶШ§Щ… ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ .dll Щ…ШұШЁЩҲШ· ШЁЩҮ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ Щ…ШӘШҜЩҠ ШӘШ№ШұЩҠЩҒ Щ…ЩҠ ЩғЩҶЩҠЩ… ШЁЩҮ Ш§ШіЩ… LoadCultureAssmeblies ШЁЩҮ ШҙЩғЩ„ ШІЩҠШұ:
//will keep information about loaded assemblies
public List<CultureAssemblyModel> CultureAssemblies { get; set; }
//loads assmeblies in languages folder and adds their info to list
void LoadCultureAssemblies()
{
//we should be sure that list is empty before adding info (do u want to add some cultures more than one? of course u dont!)
CultureAssemblies.Clear();
//creating a directory represents applications directory\languages
DirectoryInfo dir = new DirectoryInfo(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirector y + "\\languages");
//getting all .dll files in the language folder and its sub dirs. (who knows? maybe someone keeps each culture file in a seperate folder!)
var assemblies = dir.GetFiles("*.dll", SearchOption.AllDirectories);
//for each found .dll we will create a model and set its properties and then add to list for (int i = 0; i < assemblies.Count(); i++)
{
CultureAssemblyModel model = new CultureAssemblyModel() { DisplayText = assemblies[i].Name.Split('.', '_')[2], Culture = assemblies[i].Name.Split('.', '_')[1], Name = assemblies[i].Name, XamlFileName =assemblies[i].Name.Substring(0, assemblies[i].Name.LastIndexOf(".")) + ".xaml" };
CultureAssemblies.Add(model);
}
}
Ш§Ш·Щ„Ш§Ш№Ш§ШӘ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶЩҠШ§ШІ Ш§ШІ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ .dll Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҶШҜЩҮ ШҙШҜЩҮ ЩҲ ШҜШұ Щ„ЩҠШіШӘ ЩҶЪҜЩҮШҜШ§ШұЩҠ Щ…ЩҠ ШҙЩҲЩҶШҜ. ШЁШұШ§ЩҠ ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠШҙ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҶ ЩҶШ§Щ… ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ ШҜШұ ComboBox ЩғШ§ЩҒЩҠ Ш§ШіШӘ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ Щ„ЩҠШіШӘ ШұШ§ ШЁЩҮ Ш№ЩҶЩҲШ§ЩҶ ItemsSource ЩӮШұШ§Шұ ШҜЩҮЩҠЩ…:
comboboxLanguages.ItemsSource = CultureAssemblies;
ШЁШ§ handle ЩғШұШҜЩҶ ШұЩҲЩҠШҜШ§ШҜ selectionChanged Щ…ШұШЁЩҲШ· ШЁЩҮ ComboBox ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ Ш§ЩҶШӘШ®Ш§ШЁ ШҙШҜЩҮ ШұШ§ ШЁЩҮ Щ…ШӘШҜ LoadCulture ЩғЩҮ ШҜШұ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ App.cs (ЩғЩ„Ш§Ші Ш§ШөЩ„ЩҠ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ) ШӘШ№ШұЩҠЩҒ ЩғШұШҜЩҮ Ш§ЩҠЩ… Ш§ШұШіШ§Щ„ Щ…ЩҠ ЩғЩҶЩҠЩ…:
//loads selected culture
public void LoadCulture(CultureAssemblyModel culture)
{
//setting current culture of applpications main thread to selected one.
System.Threading.Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentUICul ture = new System.Globalization.CultureInfo(culture.Culture);
System.Threading.Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCultu re = new System.Globalization.CultureInfo(culture.Culture);
//creating a FileInfo object represents .dll file of selected cultur
FileInfo assemblyFile = new FileInfo("languages\\" + culture.Name);
//loading .dll into memory as a .net assembly
var assembly = Assembly.LoadFile(assemblyFile.FullName);
//getting .dll file name
var assemblyName = assemblyFile.Name.Substring(0, assemblyFile.Name.LastIndexOf("."));
//creating string represents structure of a pack uri (something like this: /{myassemblyname;component/myresourcefile.xaml}
string packUri = string.Format(@"/{0};component/{1}", assemblyName, culture.XamlFileName);
//creating a pack uri
Uri uri = new Uri(packUri, UriKind.Relative);
//now we have created a pack uri that represents a resource object in loaded assembly
//and its time to load that as a resource dictionary (do u remember that we had resource dictionary in culture assemblies? don't u?)
var dic = Application.LoadComponent(uri) as ResourceDictionary;
dic.Source = uri;
//here we will remove current merged dictionaries in our resource dictionary and add recently-loaded resource dictionary as e merged dictionary
var mergedDics = this.Resources.MergedDictionaries;
if (mergedDics.Count > 0)
mergedDics.Clear();
mergedDics.Add(dic);
}
void comboboxLanguages_SelectionChanged(object sender, SelectionChangedEventArgs e)
{
var selectedCulture = (CultureAssemblyModel)comboboxLanguages.SelectedIt em;
App app = Application.Current as App;
app.LoadCulture(selectedCulture);
}
Щ…ШӘШҜ LoadCulture ШЁШ§ ЪҜШұЩҒШӘЩҶ Щ…ШҙШ®ШөШ§ШӘ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ Ш§ШұШіШ§Щ„ ШҙШҜЩҮШҢ culture ШіЩҠШіШӘЩ… ШұШ§ ШЁЩҮ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ Щ…ЩҲШұШҜ ЩҶШёШұ ШӘШәЩҠЩҠШұ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҮ ЩҲ resource dictionary Щ…ШұШЁЩҲШ· ШЁЩҮ ШўЩҶ ШұШ§ Ш§ШІ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ .dll ШўЩҶ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ load ЩғШұШҜЩҮ ЩҲ ШўЩҶ ШұШ§ ШЁШ§ resource dictionary ЩҒШ№Щ„ЩҠ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ Ш¬Ш§ЩҠЪҜШІЩҠЩҶ Щ…ЩҠ ЩғЩҶШҜ. Button ЩҮШ§ ЩғЩҮ Щ…ШӯШӘЩҲШ§ЩҠ Ш®ЩҲШҜ ШұШ§ ШЁЩҮ ШҙЩғЩ„ dynamic Ш§ШІ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ resource dictionary ШҜШұЩҠШ§ЩҒШӘ Щ…ЩҠ ЩғШұШҜЩҶШҜ ШӯШ§Щ„Ш§ Ш§ШІ ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„ ЩҒШ§ЩҠЩ„ Ш¬Ш§ЩҠЪҜШІЩҠЩҶ ШҙШҜЩҮ Ш®ЩҲШ§ЩҮЩҶШҜ ЪҜШұЩҒШӘ.
ЩғШ§Шұ Ш§ЩҶШ¬Ш§Щ… ШҙШҜ!
Ш§ШІ Щ…ШІЩҠШӘ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Ш§ЩҠЩҶ ШұЩҲШҙ Щ…ЩҠ ШӘЩҲШ§ЩҶ ШЁЩҮ WPF-Native ШЁЩҲШҜЩҶШҢ ШіШ§ШҜЪҜЩҠ ШҜШұ ЩҫЩҠШ§ШҜЩҮ ШіШ§ШІЩҠШҢ ЩӮШ§ШЁЩ„ЩҠШӘ load ЩғШұШҜЩҶ ЩҮШұ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ Ш¬ШҜЩҠШҜЩҠ ШҜШұ ШІЩ…Ш§ЩҶ Ш§Ш¬ШұШ§ ШЁШҜЩҲЩҶ ЩҶЩҠШ§ШІ ШЁЩҮ ЩғЩҲЪҶЩғ ШӘШұЩҠЩҶ ШӘШәЩҠЩҠШұ ШҜШұ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ Ш§ШөЩ„ЩҠ ЩҲ ЩҮЩ…ЪҶЩҶЩҠЩҶ ЩҫШҙШӘЩҠШЁШ§ЩҶЩҠ ЩғШ§Щ…Щ„ Ш§ШІ ЩҶЩ…Ш§ЩҠШҙ ШІШЁШ§ЩҶ ЩҮШ§ЩҠ Щ…Ш®ШӘЩ„ЩҒ Ш§ШІ Ш¬Щ…Щ„ЩҮ ЩҒШ§ШұШіЩҠ Ш§ШҙШ§ШұЩҮ ЩғШұШҜ.
Щ„ЫҢЩҶЪ© Ш§ЩҲЩ„ PDF ЩҲ Щ„ЫҢЩҶЪ© ШҜЩҲЩ… ЩҶЩ…ЩҲЩҶЩҮ ШЁШұЩҶШ§Щ…ЩҮ ЩҮШіШӘЩҶШҜ.





 ЩҫШ§ШіШ® ШЁШ§ ЩҶЩӮЩ„ ЩӮЩҲЩ„
ЩҫШ§ШіШ® ШЁШ§ ЩҶЩӮЩ„ ЩӮЩҲЩ„











 Microsoft.VisualBasic.ApplicationServices
Microsoft.VisualBasic.ApplicationServices